
Retinitis Pigmentosa and Retinal Prosthesis
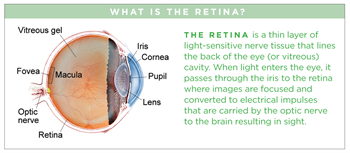
Retinitis pigmentosa (RP) refers to a group of inherited (passed down from parents) diseases causing retinal degeneration and blindness. The retina lines the back inside wall of the eye and is responsible for capturing and processing images. Individuals with RP lose their vision because photoreceptor (light-sensing) cells of the retina gradually degenerate and then die. In most forms of RP (rod-cone dystrophy), night blindness is one of the earliest and most frequent symptoms.
Symptoms
Retinitis pigmentosa symptoms can start as early as childhood, but side effects may not begin to take precedence until early adulthood. Symptoms include:
- Night blindness
- Loss of peripheral (side) vision
- Cataracts
- Loss of central vision
In some instances, the disorder progresses slowly and may be found on routine examination.
Symptoms in detail
In later stages, centrally located photoreceptors (cones) responsible for color and sharp central vision degenerate, resulting in loss of color perception and central vision. RP is typically diagnosed in late adolescence and young adulthood. It gradually progresses, but the rate of progression and degree of visual loss vary from person to person. Most people with RP are legally blind by age 50; they experience “tunnel vision,” with a central visual field of less than 20 degrees in diameter.
Causes
RP has been associated with more than 100 different gene mutations. Genes determine the type and amount of proteins in cells. With a mutated RP gene, photoreceptors or their supporting cells have defective proteins, or have too much or too little of a particular protein. This causes abnormal function and eventual death of retinal photoreceptors. These mutations are either inherited or are acquired (ie, occur in the early stages of development before birth).
Diagnostic testing
Diagnosis of RP relies on the documentation of progressive loss of peripheral (side) vision (with a test called visual field perimetry) and demonstration of ocular (eye) changes associated with retinal degeneration. Retinal examination shows pigmentary changes referred to as bone spicules and optical coherence scanning confirms retinal thinning. Later in the diseases, cataracts (clouding in the eye’s lenses) can occur. Additional testing with electroretinography (ERG), which measures the electrical responses of the retina to light, confirms the RP diagnosis by evaluating photoreceptors’ function.
Genetic testing, although not necessary to diagnose RP, helps with attaining an accurate diagnosis and also potentially assessing the risk of passing the disorder from parents to their children. Sometimes, laboratory tests are useful in excluding other diseases that may look like RP or in detecting conditions associated with RP.
Treatment and prognosis
No cure is yet available for RP. Efforts to slow down the progression of RP, as well as gene therapy to cure the disease before it gets worse, are being actively pursued. However, once the photoreceptors die, the only options are to either transplant new photoreceptors or bypass them. Photoreceptor transplantation continues to be studied but so far, there are no results that show a clear benefit.
Bypassing the photoreceptors is based on the finding that, although photoreceptors die in RP, their connections to the brain are mostly preserved.
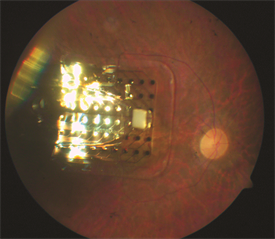
Figure 1. Retinal Prosthesis Image courtesy of University of Southern California |

Figure 2. ARGUS II Image courtesy of University of Southern California |
Bypassing photoreceptors is currently being attempted using gene therapy to make the remaining cells light sensitive (optogenetics) but this has still not entered clinical trials.
A second method to restore vision in eyes with RP is to use microelectronic chip technologies to convert light rays to neuronal impulses that can be conveyed to the brain via the preserved connections. This method, referred to as retinal prosthesis, artificial vision, retinal chip, and bionic eye, has been used in limited patients, but Argus II pictured above is no longer available on the market. Higher resolution retinal prosthesis are being developed. Another approach that is being investigated is to use a small camera embedded in glasses attached wirelessly to electrodes on the brain in the visual cortex. This is another potential way to convert electrical signals from visible objects to achieve vision directly within the brain.
Many novel methods have been proposed to connect a retinal prosthetic device to a blind eye. Multiple research groups around the world are working to find the best way to achieve artificial vision with retinal prosthesis and direct input to the brain.
These amazing technologies are off to a promising start. Researchers now face the challenge of refining the focus of the retinal chip to enable patients to read, recognize faces and identify colors. Ongoing research activities in bioelectronics and neuroscience laboratories are likely to provide answers to many of these challenges and to help more blind people see through artificial vision
